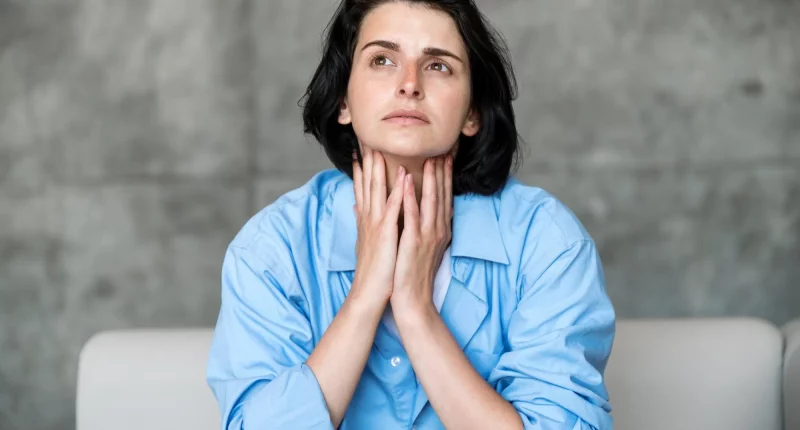
Cervical lymphadenitis is an inflammation of the lymph nodes situated in the neck. It often results from infections, like viral, bacterial, or fungal, and can cause inflammation, pain, and sensitivity in the affected area. Common causes include upper respiratory infections, like mononucleosis or strep throat, as well as dental infections and skin conditions. Treatment typically involves addressing the underlying infection with antiviral or antibiotic medications, along with supportive care to manage symptoms. If the condition is chronic or recurrent, further investigation may be needed to eliminate more serious basic issues.
Causes
Cervical lymphadenitis is frequently caused by infections. Bacterial infections, like staphylococcal infections, are frequent culprits and often arise from conditions like strep throat or skin infections. Viral infections, including those caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (which causes mononucleosis) and cytomegalovirus, can also lead to cervical lymphadenitis. Additionally, fungal infections and parasitic diseases, though less common, may contribute to lymph node inflammation in the neck.
Apart from infections, other causes of cervical lymphadenitis include dental problems, like severe gum infections or abscesses, which can spread to nearby lymph nodes. Skin conditions, like impetigo or cellulitis, may also result in lymph node swelling. In some cases, malignancies like metastases or lymphomas from cancers elsewhere in the body may cause continuous or unusual lymphadenitis. Chronic or repeated cases may necessitate further diagnostic evaluation to detect any serious underlying conditions.
Symptoms
The symptoms of cervical lymphadenitis usually include tenderness and swelling in the lymph nodes located in the neck. This swelling can differ in size from tiny, pea-sized lumps to larger, noticeable masses. The impacted lymph nodes may feel hot or warm to the touch and may be accompanied by inflammation or redness of the skin overlying the nodes. Patients often experience pain in the neck area, which can range from mild discomfort to serious pain, particularly when pressing on the swollen nodes or moving the head.
Additional symptoms can involve fever, which is a common response to infection, and general malaise, like extreme tiredness and weakness. In some cases, there may be symptoms related to the basic cause of the lymphadenitis, like discomfort throat, difficulty swallowing, or oral ulcers if the infection originates from a dental issue. Continuous or serious symptoms may indicate a more serious condition, requiring prompt medical evaluation and intervention.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing cervical lymphadenitis involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider. The process usually starts with a thorough medical history and physical examination to assess the place, size, and sensitivity of the swollen lymph nodes.
Diagnostic tests may include blood tests to detect signs of inflammation or infection, and imaging studies like ultrasound, CT, or MRI scans to evaluate the extent and features of the swollen lymph node. In some episodes, a lymph node biopsy or fine needle aspiration may be performed to obtain tissue samples for further analysis, particularly if there is a concern about cancer or an unusual presentation. The outcomes of these tests help determine the basic cause of lymphadenitis and guide appropriate treatment.
Treatment
The treatment of cervical lymphadenitis mainly aims to address the basic cause of the inflammation. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are recommended to target the specific pathogen detected through culture or clinical suspicion. Pain relief and symptom management are also important, and over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help decrease fever and pain. Warm compresses applied to the affected area may provide additional comfort and alleviate inflammation.
If the lymphadenitis is caused by viral infections or other non-bacterial sources, treatment typically involves supportive care, like hydration, rest, and analgesics to manage symptoms. In cases where skin or dental infections are the root cause, addressing the primary infection with appropriate treatment—like dental procedures or topical treatments—is essential. For chronic or repeated cases, further evaluation may be necessary to eliminate underlying conditions, like cancerous, which may need specialized treatment or referral to an oncologist.
Complications
Cervical lymphadenitis can cause several complications if not properly managed. One common complication is the formation of an abscess, which occurs when fluid accumulates within the swollen lymph node. This can cause increased pain, inflammation, and redness, and may need drainage through a surgical procedure or needle aspiration. Additionally, serious or untreated infections can cause the spread of infection to nearby tissues, potentially resulting in cellulitis or more widespread infections.
Another potential complication is the development of chronic lymphadenitis, where the inflammation persists over a long period, potentially leading to scar tissue formation and lasting discomfort. In some cases, persistent lymphadenitis may indicate an underlying serious condition, like lymphoma or other cancers, which need prompt diagnosis and intervention. Addressing these complications often involves more intensive medical interventions and ongoing observation to ensure effective management and recovery.
Prevention
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regular hand washing and maintaining proper oral hygiene can decrease the risk of infections that might lead to cervical lymphadenitis.
- Address Infections Promptly: Seek medical attention for infections like sore throats, dental problems, or skin infections to prevent them from spreading to the lymph nodes.
- Vaccination: Stay up-to-date with vaccinations for diseases that can cause lymphadenitis, like mumps or measles.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Effectively manage chronic health conditions that could increase susceptibility to infections, like diabetes.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Refrain from sharing utensils, towels, or other personal items that can spread infections.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can help detect and address potential sources of infection early, reducing the risk of developing lymphadenitis.
Summary
Cervical lymphadenitis is inflammation of the neck’s lymph nodes, commonly caused by infections like viral, bacterial, or fungal. Symptoms include swollen, sensitive nodes, pain, fever, and related issues depending on the infection source. Diagnosis involves a medical history review, physical examination, and possibly imaging or biopsy to detect the cause. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying infection with antibiotics or supportive care, along with symptom management. Complications can include abscess formation, spread of infection, or chronic lymphadenitis, potentially indicating more serious conditions. Effective management requires addressing both the symptoms and any underlying causes to prevent further issues.