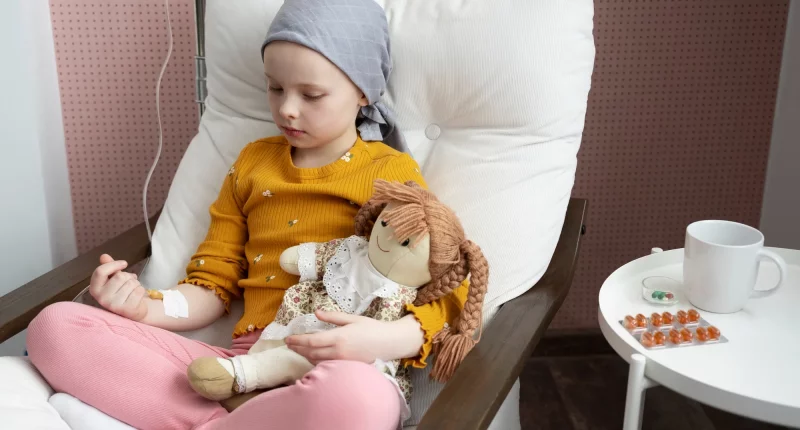
Burkitt lymphoma is a rare and fast-growing type of cancer that mostly affects children. It belongs to a group of cancers called non-Hodgkin lymphomas, which start in a type of white blood cell known as lymphocytes. These cells are important for the body’s defense as opposed to diseases.
Burkitt lymphoma was first found in children living in Africa and is still closely connected to that region. This cancer is often connected to other health issues, such as the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and certain genetic changes in the chromosomes.
Even though Burkitt lymphoma is aggressive, meaning it grows and spreads quickly, it is generally treatable with modern medical therapies.
Types
Endemic Burkitt Lymphoma
This type is most common in Africa and is closely associated with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which also leads to infectious mononucleosis (mono). It often appears as a tumor in the jaw. Outside of Africa, endemic Burkitt lymphoma is very rare.
Sporadic Burkitt Lymphoma
Unlike the endemic type, sporadic Burkitt lymphoma can be found worldwide. The most common sign of this type is a tumor in the abdomen.
Immunodeficiency-Related Burkitt Lymphoma
This form occurs in individuals with weakened immune systems. It commonly occurs in people with HIV/AIDS or those born with immune system problems. It can also affect individuals who take drugs that weaken the immune system after an organ transplant.
Symptoms of Burkitt Lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma is known for being a rapidly developing tumor in the body, which means symptoms can appear very quickly. One of the first signs is the rapid inflammation of lymph nodes in the neck and head. This swelling happens quickly but is usually painless. In the endemic form of Burkitt lymphoma, which is commonly found in Africa, the swelling often affects the jaw and can lead to noticeable changes in the facial bones.
In the more common sporadic form of Burkitt lymphoma, particularly seen in the United States, the disease often begins in the abdomen. However, Burkitt lymphoma may also start in other parts of the body, such as the kidneys, bowel, nervous system, or reproductive organs.
In addition to these specific symptoms, there are some general symptoms that people with Burkitt lymphoma might experience. These include night sweats, fever, unintentional weight loss, extreme tiredness, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms can help in identifying the disease early, allowing for quicker diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Burkitt Lymphoma
Scientists are still unsure about the exact causes of Burkitt lymphoma. However, they do know that this disease most frequently affects children and is the leading form of childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
In the United States, sporadic Burkitt lymphoma makes up about 30 percent of childhood lymphomas. In Africa, endemic Burkitt lymphoma is responsible for 30 to 50 percent of all infancy cancers.
A strong link has been found between endemic Burkitt lymphoma and the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which is known to cause infectious mononucleosis. Other risk elements for developing Burkitt lymphoma include having an immune system weakened by diseases like HIV or staying in areas where malaria is prevalent.
Diagnosis of Burkitt Lymphoma
To diagnose Burkitt lymphoma, healthcare providers usually start with a biopsy of the lymph nodes or bone marrow. A biopsy involves taking a tiny part of tissue and examining it in a laboratory. A pathologist looks at the tissue to see if it contains cancer cells and to identify the kind of cancer.
Besides the biopsy, healthcare providers might use several other tests to diagnose Burkitt lymphoma:
- Physical Exam: The healthcare provider will check the body for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else unusual.
- PET Scan or CT scan: These imaging tests provide detailed pictures of the inside of the body to look for tumors.
- X-ray: This can help detect any abnormalities in the chest area.
- Spinal Tap: Also known as a lumbar puncture, this test involves taking a sample of the fluid around the spine to check for cancer cells.
- Blood Tests: These can give information about overall health and detect substances that might indicate cancer.
These tests help healthcare providers confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the disease, which is essential for planning the right treatment.
Treatment for Burkitt Lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma is highly treatable, but because it develops so quickly, it’s important to start treatment as soon as possible. If left untreated, this cancer can rapidly become very serious.
The main treatment for Burkitt lymphoma is intensive chemotherapy. This involves using powerful drugs to kill cancer cells. Heals often use chemotherapy drugs in combination to get the best results. One of these drugs is rituximab can improve treatment outcomes and decrease side effects.
If chemotherapy doesn’t work, healthcare providers might suggest a bone marrow transplant. This procedure replaces damaged bone marrow with healthy marrow, which can help the body produce new blood cells and fight the cancer more effectively.
Outlook
Burkitt lymphoma is normally positive if medication begins quickly. More than 50% of patients can be restored with intensive chemotherapy.
Children with Burkitt lymphoma have an especially favorable outlook. For those diagnosed at an early stage, the long-term living rate is over 90%. Even for children and adolescents with more advanced stages of the disease, the survival rate is still high, ranging from 80 to 90 percent.
In contrast, the outlook is more challenging for older individuals because they often can’t bear the intensive chemotherapy required for treatment. This means that survival rates are lower for elderly patients.
If Burkitt lymphoma relapses or comes back after treatment, the outlook is generally poor.
Managing the Burkitt lymphoma
Coping with a cancer diagnosis like Burkitt lymphoma can be tough. Patients can take care of themselves by focusing on a healthy lifestyle: eating well, staying active through exercise, and getting plenty of rest. It’s important for caregivers of infants with malignancy to do the same, ensuring they stay healthy and strong to support their loved ones.
Managing stress is also crucial. Individuals experiencing stress due to their diagnosis can try activities like yoga, meditation, massage therapy, or even writing about their feelings and experiences. These methods can help decrease stress and promote emotional well-being during treatment and recovery.
Summary
Burkitt lymphoma is a rare and aggressive type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, primarily affecting children and linked to factors like Epstein-Barr virus and weakened immune systems. Diagnosis involves biopsies and various tests to confirm the presence and extent of the cancer. Treatment focuses on intensive chemotherapy, often including rituximab, with the option of bone marrow transplants for non-responsive cases.
Prognosis is generally positive with prompt treatment, especially in children, though older adults may face greater challenges. Coping strategies include maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing stress through activities like meditation and yoga.