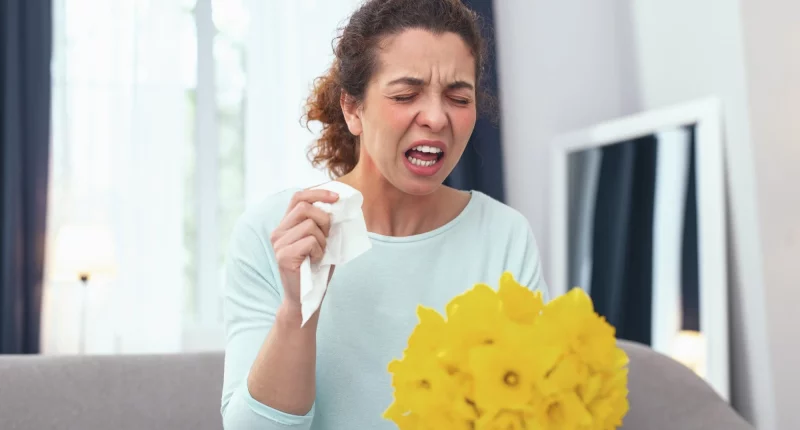
Anaphylaxis is a really serious allergic reaction. It can happen when you eat certain foods, get stung by insects, or because of other things. When someone has anaphylaxis, they might notice swelling, redness (like hives), and have trouble breathing. Sometimes, it can quickly get worse, leading to a condition called anaphylactic shock, which can even be deadly.
In the United States, about 200,000 people end up in the hospital every year because of food allergies, as stated by a group called the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America (AAFA). But it’s not just food that can cause these reactions. Medicines and insect bites can do it too.
The AAFA says that more than 50 million individuals in the U.S. have allergic reactions each year. Allergies are a big reason why people get sick a lot and have to see doctors often.
Here, we will discuss about what it’s like to have a really bad allergic reaction, like anaphylaxis. We will also explain why it happens and what’s going on inside the body when it does.
Causes
Anaphylaxis occurs when the body perceives a foreign substance as a significant danger to health. This heightened reaction can lead to severe consequences. The most frequent triggers for such reactions are medications, certain foods, and insect bites.
Among the foods commonly associated with triggering allergic reactions are eggs, milk, fish, crustacean shellfish, soy, peanuts, wheat, and tree nuts. These substances can provoke intense immune responses in susceptible individuals.
Anything that induces an allergic reaction is termed an allergen. Even small amounts of these allergens can prompt severe reactions in some people. This heightened sensitivity underscores the importance of careful management and avoidance of potential triggers for those prone to anaphylaxis.
Managing Anaphylaxis
When the body encounters something it’s allergic to, it releases a lot of histamine, which is like a signal that tells the body to react.
This reaction can cause a few things to happen:
- The blood vessels get wider, which can make blood pressure suddenly drop.
- Some people might even faint or lose consciousness because of it.
- They might also go into shock, which is a really serious condition.
When someone’s having anaphylaxis, their airways can get smaller, making it hard to breathe.
Also, their blood vessels might start leaking, leading to swelling called edema, where fluid builds up.
Sometimes, this reaction happens right away after touching the allergen. But for some people, it might not show up until hours later, or even days afterward, though that’s pretty rare.
Symptoms
The signs of anaphylaxis are serious and often require immediate medical help. Specific symptoms can vary depending on what a person is allergic to and what caused the reaction. These symptoms might include things like a stuffy or runny nose, an itchy throat or mouth, or feeling like your tongue is swollen and heavy. You might also have trouble swallowing or feel like something is stuck in your throat.
Other symptoms can involve coughing, a hoarse voice, wheezing, or finding it hard to breathe, which can feel like tightness in your throat or chest. You might feel pain in your chest or stomach, along with cramps, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Your skin might swell, itch, and turn red, sometimes with hives or a rash.
Feeling anxious or like something really bad is about to happen is common during anaphylaxis. Your hands, feet, lips, eyes, and even genitals might swell up. Your skin might turn pale blue from hypotension, and you might feel faint or dizzy. In severe cases, you could lose consciousness, and shock can even happen, which is life-threatening.
Sometimes, you might also have red, watery eyes, a headache, or cramps in your uterus. Severe problems with breathing or a sudden drop in blood pressure can cause shock, which is extremely dangerous and needs urgent medical attention.
First Aid
When someone is having a serious allergic reaction, it’s crucial to get them help right away. Medical attention for anaphylaxis involves a few important steps to try to help them before medical professionals arrive.
The first thing to do is to remove whatever caused the allergic reaction, if you can, and then ask for emergency help. It’s important to keep the person comfortable, so try to keep them cool and loosen any tight clothing.
If they feel like they might faint, help them sit down, repose, or lie flat. It’s also a good idea to ask if they’ve had bad allergic reactions before, just in case. If they have medicine for their allergies, like an EpiPen, help them use it. Stay with them, and try to keep them calm until help arrives.
People who’ve had serious allergic reactions before might carry an injector with them that has a dose of a medicine called epinephrine, which helps with allergic reactions. This injector can be a lifesaver in an emergency.
Assisting Breathing
When someone’s having trouble breathing, there are a few things you can do to help until help arrives.
First, it’s important to make sure they’re sitting up a bit and leaning forward. This can make breathing easier for them.
But if they start feeling like they might pass out, it’s better for them to lie down flat with their legs up.
If they do pass out, make sure their head is lean back so they can keep breathing.
Stay with them and keep an eye on how they’re doing until the doctors come. When they get there, try to tell them what caused the reaction and if the person got any medicine.
If you can, try to keep whatever caused the reaction away from the person, especially when they’re being taken to the hospital.
If the person is not breathing, you might need to do something called CPR to help them. Keep doing chest compressions until the doctors take over.
Treatment
When someone has a really bad allergic reaction, they need quick help. Doctors give them a shot of a medicine called epinephrine, also known as adrenaline.
Here’s how it helps:
- It makes blood vessels smaller, which reduces swelling and raises blood pressure.
- It relieves the muscles over the lungs so the person can breathe better.
- It stops the body from releasing more chemicals that make the reaction worse.
Most of the time, this treatment works well, and the person starts feeling better right away. But if they don’t improve quickly, they might need another shot after about 10 minutes.
Sometimes, even after the symptoms go away, they can come back. In that case, the person might need to stay in the hospital for a day to make sure they’re okay.
If the allergic reaction isn’t as bad, the doctor might give them different shots like antihistamines or corticosteroids to help.
Prevention
Anaphylaxis is a really serious emergency. Sometimes, a person can suddenly have this reaction to something they’ve never had a problem with before.
Allergic reactions can be tricky because you never know when they might happen. That’s why it’s super important to stay away from anything you know you’re allergic to, even if it hasn’t made you really sick before.
But it’s not always easy to avoid everything that might set off an allergic reaction. That’s why some people have to carry special medicine with them and put on a bracelet that tells others about their allergies.
If someone has had bad allergic reactions before, it’s really important to tell the people around them, like family, friends, and even people at work or school, what things can cause the reaction. This helps everyone be prepared to help if something goes wrong.
Take Away
It’s really serious if someone has anaphylaxis – it could even be life-threatening. If someone has a really bad allergic reaction like this, they need to see a doctor right away.
Knowing what to do in this kind of emergency can be really important and might even save someone’s life. So, it’s super important to learn about the symptoms and what you should do if someone you know has a severe allergic reaction.
Summary
Anaphylaxis is a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction that demands immediate medical attention. Understanding the symptoms, triggers, and appropriate responses is crucial in managing this emergency situation effectively. Prevention strategies, such as avoiding known allergens and carrying necessary medications, play a vital role in reducing the risk of anaphylaxis.
Additionally, clear communication with friends, family, and others about one’s allergies can help ensure swift and appropriate assistance if an allergic reaction occurs. By being proactive and knowledgeable about anaphylaxis, individuals can better protect themselves and others, potentially saving lives in critical situations.