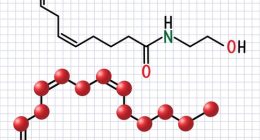
In the realm of sports nutrition, the role of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), has garnered significant attention due to their potential benefits for athletic performance and recovery. Researchers Maja Tomczyk, Jeffery L Heileson, Mirosław Babiarz, and Philip C Calder have explored this topic extensively in their study titled “Athletes Can Benefit from Increased Intake of EPA and DHA-Evaluating the Evidence.” Their research highlights how EPA and DHA, primarily found in fatty fish such as mackerel, herring, salmon, sardines, and certain algae, are critical yet under-consumed nutrients in the diets of athletes.
The study delves into the various advantages of EPA and DHA, which include moderating inflammation, supporting nervous system function, helping maintain muscle mass post-injury, and enhancing training adaptation. The authors address the challenges related to the inconsistent levels of these fatty acids in natural sources and the general inadequacy in athletes’ diets. They also discuss the potential of supplements as alternative sources to meet the nutritional needs in regards to EPA and DHA.
This paper provides a comprehensive overview, evaluating existing evidence on the efficacy of EPA and DHA intake in improving athletic performance and recovery, ultimately suggesting that athletes might benefit from considering supplements to achieve optimal levels of these essential nutrients.
The importance of omega-3 fatty acids in human nutrition has been recognized for decades, with an array of research underscoring their benefits for cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and overall inflammatory response. However, the specific impact of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), on sports performance and recovery has become an intriguing subject for sports nutritionists and researchers only more recently.
Athletes are constantly searching for ways to enhance performance and accelerate recovery. Conventional dietary focus often includes macronutrients such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats; however, the role of specific micronutrients like EPA and DHA is less emphasized but increasingly recognized as crucial. The metabolic demands of high-intensity training and the physical stress it places on the body makes nutrition a critical aspect of an athlete’s regimen. This recognition has steered Maja Tomczyk, Jeffery L Heileson, Mirosław Babiarz, and Philip C Calder to explore how increased intake of these polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) could enhance athletic performance and support recovery.
Previous studies have shown that EPA and DHA play a significant role in the biochemical functioning of the body. They are integral components of cell membranes, affect the function of cell receptors, and provide starting points for producing hormones that regulate blood clotting, contraction and relaxation of artery walls, and inflammation. Given the strenuous nature of athletic activities, which often result in muscular injuries and chronic inflammation, EPA and DHA could potentially be pivotal in promoting better recovery processes.
Research prior to the study conducted by Tomczyk et al. suggested that these fatty acids could help mitigate the inflammatory responses typically observed after intense exercise sessions. Furthermore, DHA is particularly noted for its involvement in brain health and function, a benefit of interest to athletes engaged in sports requiring high levels of cognitive function and mental precision.
Natural sources of EPA and DHA are limited, predominantly found in oily fish and certain algae, leading to challenges in obtaining sufficient amounts from diet alone. This is especially true given modern diets, which are frequently deficient in these nutrients. For athletes, who may require higher levels of these nutrients than non-athletes, this can present a significant dietary challenge.
Tomczyk and colleagues aim to bridge the gap in literature by providing a comprehensive analysis of the role of EPA and DHA in sports nutrition. By evaluating the current evidence and identifying gaps in knowledge, their research seeks to underscore the potential benefits that these fatty acids hold for athletic performance, stimulate further research, and adjust dietary recommendations for athletes accordingly. The ultimate goal is to establish a clearer understanding of how increased intake of EPA and DHA could be implemented effectively in the dietary patterns of athletes to optimize their performance and recovery.
The methodology employed in the study conducted by Maja Tomczyk, Jeffery L. Heileson, Mirosław Babiarz, and Philip C. Calder involved an integrative review of existing literature, coupled with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies focusing on the impact of EPA and DHA on athletic performance and recovery. This approach helped to synthesize a wide range of data to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
### Literature Review
Initially, the researchers conducted an extensive literature review, sourcing relevant articles, studies, and prior research from various scientific databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar. The inclusion criteria focused on studies published in peer-reviewed journals that specifically investigated the effects of EPA and DHA supplementation on athletic performance, recovery, inflammation, muscle injury, nervous system function, and mental health in sports settings. Articles were filtered based on their relevance to the topic, the age of the study, and the sample size of the populations studied.
### Selection of Studies
After the initial collection of articles, the researchers applied more stringent criteria to narrow down their sources to the most relevant and reliable studies. They excluded studies that did not clearly define the dosage of EPA and DHA, those that did not have a control group, and studies where the subjects were non-athletes. This ensured that the findings were applicable to athletic populations and that the results could be more specifically attributed to the effects of EPA and DHA.
### Meta-Analysis
For the meta-analysis, the team selected randomized controlled trials that directly compared the outcomes of EPA and DHA supplementation with a control group not receiving supplementation or receiving a placebo. The key outcomes analyzed included markers of inflammation, muscle recovery post-exercise, cognitive function, and overall performance enhancement. The meta-analytical techniques employed allowed the researchers to quantitatively combine the results from different studies and compute the average effect sizes, providing a more powerful analysis of the impact of EPA and DHA on the specified outcomes.
### Observational Studies
In addition to RCTs, observational studies were included to examine the long-term effects of natural EPA and DHA intake from dietary sources on athletic performance and health outcomes. These studies provided insights into the real-world applications and adherence to diets rich in EPA and DHA, as well as the potential epidemiological correlations between natural intake levels and performance metrics.
### Data Synthesis and Interpretation
The final phase of the methodology involved synthesizing the data collected from both the meta-analysis and the observational studies. This synthesis involved a qualitative review of the findings, drawing connections between varied studies and identifying patterns and trends that emerged. The researchers also assessed the quality and biases of the studies included, which helped in interpreting the results with a critical perspective.
The comprehensive approach taken in the study by Tomczyk and colleagues ensured a robust analysis of the available evidence, allowing them to draw nuanced conclusions about the potential benefits of EPA and DHA for athletes. This methodology not only highlighted the direct impacts of supplementation but also provided a broader perspective on how dietary intake of these fatty acids could influence long-term athletic performance and recovery.
### Key Findings and Results
The study conducted by Maja Tomczyk and colleagues revealed several key insights into the impact of EPA and DHA on athletic performance and recovery. Here are the primary findings from their thorough investigation:
1. **Inflammation Reduction**: One of the most significant results indicated that EPA and DHA supplementation effectively reduced markers of inflammation in athletes. This is particularly crucial following high-intensity exercise, which can induce acute inflammatory responses. The meta-analysis showed that athletes receiving these supplements had lower levels of inflammatory cytokines compared to those who did not receive supplementation. This suggests that EPA and DHA can help mitigate the inflammatory process post-exercise, potentially leading to quicker recovery and better performance in subsequent sessions.
2. **Enhanced Muscle Recovery**: The reviewed evidence highlighted that EPA and DHA intake was associated with improved muscle recovery mechanisms. This was observed through decreased muscle soreness and improved muscle function tests post-exercise in athletes who consumed these fatty acids compared to controls. The recovery benefits are attributed to the anti-inflammatory properties of EPA and DHA, which may help in faster repair and less muscle damage over time.
3. **Cognitive Function and Mental Health**: The study also pointed out the beneficial effects of EPA and DHA on cognitive functions, which are essential for athletes in sports requiring quick decision-making and strategic thinking. Supplements containing these omega-3 PUFAs were linked to improved reaction times and mental sharpness. Additionally, some studies suggested potential benefits in mood stabilization and reduction of anxiety levels, which are critical under competitive pressures.
4. **Cardiovascular Health**: While the primary focus was on performance and recovery, the research also reinforced the role of EPA and DHA in promoting cardiovascular health. This is beneficial not only for long-term health outcomes but also for enhancing aerobic capacity and endurance performance. Improved heart health facilitates efficient blood flow and nutrient delivery to muscles during exercise.
5. **Dosage and Source Considerations**: An important aspect of the research was identifying the optimal doses of EPA and DHA for athletic benefits, as well as the best sources. Supplements were shown to be effective in reaching the required intake levels that might be difficult to achieve through diet alone, especially among athletes who might require higher dosages to counteract exercise-induced stress and inflammation.
The review acknowledged variability in study results, which could be due to differences in supplement doses, the athletic discipline of participants, baseline nutrient status of the individuals, and their overall diet. Despite these variations, the general consensus supported the positive role of EPA and DHA supplementation in enhancing athletic outcomes.
### Implications for Future Research and Dietary Guidelines
The findings from Tomczyk’s team suggest a promising area for further research and potential modifications to dietary guidelines for athletes. Future studies should explore the long-term effects of regular EPA and DHA intake, optimal dosages for different sports disciplines, and the interaction of these fatty acids with other nutrients involved in athletic performance. Additionally, there is a need to expand the research to diverse populations including different age groups, genders, and performance levels to validate and generalize the benefits observed.
With these results, the sports nutrition community is better equipped to guide athletes in optimizing their dietary patterns to include sufficient levels of EPA and DHA, potentially through both natural food sources and supplements. These findings not only highlight the importance of these nutrients in an athlete’s diet but also pave the way for more informed and specific nutritional strategies that cater to the needs of various athletic populations, enhancing their overall performance and well-being.
### Future Directions and Final Thoughts
The study conducted by Maja Tomczyk and colleagues marks a significant advance in our understanding of how EPA and DHA impact athletic performance and recovery. However, several avenues remain unexplored, and further research is necessary to fully harness the potential of these omega-3 fatty acids in sports nutrition.
#### Expanding the Scope of Research
Future studies should aim to include larger sample sizes and diverse populations, encompassing different ages, genders, and athletic disciplines. This would help in establishing more generalized conclusions and creating tailored nutritional guidelines that cater to specific needs. The longitudinal impacts of continuous intake of EPA and DHA, through both diet and supplements, also warrant detailed exploration. Such studies could help in understanding the long-term benefits and potential risks associated with prolonged omega-3 PUFA supplementation.
#### Optimizing Dosage and Formulation
Determining the optimal dosage of EPA and DHA that maximizes athletic performance and recovery remains a critical challenge. Further research should focus on identifying dose-response relationships and exploring the synergistic effects of combining omega-3 PUFAs with other nutrients, such as antioxidants and amino acids, that might enhance athletic outcomes. Additionally, the development of advanced supplement formulations that improve the bioavailability and efficacy of EPA and DHA could be pivotal.
#### Nutritional Strategies and Guidelines
Based on emerging evidence, sports nutritionists and dietitians should work to update and refine dietary guidelines to incorporate EPA and DHA recommendations more prominently. Educational initiatives should be launched to raise awareness among athletes about the benefits of omega-3 PUFAs and to guide them in selecting appropriate food sources and supplements.
#### Technological Advances in Nutritional Monitoring
The integration of technology in sports nutrition, including mobile apps and wearable devices that track nutrient intake and its effects on performance, could significantly enhance individualized nutrition planning. These tools can help athletes and coaches monitor and adjust omega-3 PUFA intake in real-time, based on specific training and recovery needs.
#### Policy and Industry Collaboration
Collaborative efforts between policymakers, food industry leaders, and sports organizations are essential to promote the availability and accessibility of high-EPA and DHA foods and supplements. Such partnerships could also be instrumental in conducting large-scale educational campaigns and supporting research efforts.
### Final Thoughts
The research spearheaded by Tomczyk and colleagues is a cornerstone that sheds light on the crucial role of EPA and DHA in enhancing athletic performance and recovery. While the study offers compelling evidence of the benefits, the full potential of these omega-3 fatty acids is yet to be completely understood and utilized in sports nutrition. As the field continues to evolve, it is essential that athletes, coaches, and nutritionists stay informed about the latest research developments and adapt their practices to incorporate these findings. With a strategic focus on optimal dosing, continual monitoring, and individualized supplementation plans, the integration of EPA and DHA into an athlete’s diet can be a game-changer in achieving peak performance and optimal health.