Carotid artery stenosis also known as carotid artery disease happens when a buildup of plaque occurs in the carotid arteries internally. These arteries are crucial because they transport oxygen-rich blood to the brain.
There are two main carotid arteries, one on each side of the collar. Each of these arteries divides into two branches: the internal and external carotid arteries. The outside of the carotid artery transports blood to the scalp and face, while the carotid artery carries blood to the brain.
A mix of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances is known as plaque. In time, this plaque can accumulate within the arteries through a process known as atherosclerosis.
As plaque builds up, it diminishes the arteries and makes it harder for blood to flow between them.
A narrowed artery can be dangerous because it may decrease or obstruct the brain’s blood flow, which can lead to a stroke.
Signs and Symptoms
Carotid artery stenosis often does not present any noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Most people with this condition may not experience any issues until it progresses. As the disease worsens, however, it can lead to significant symptoms that signal serious complications.
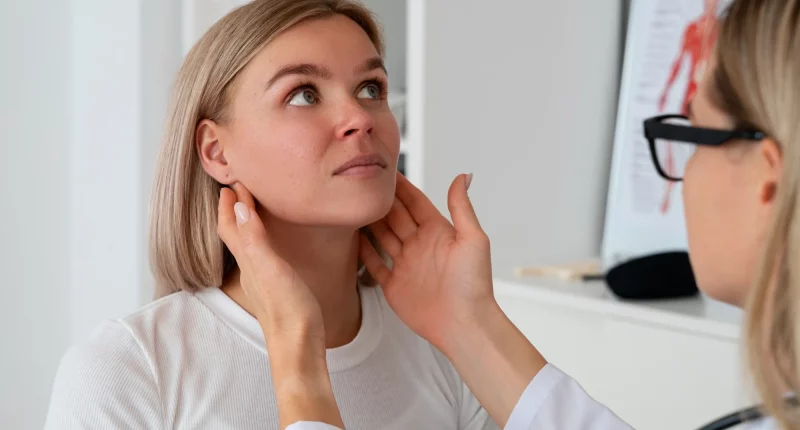
One such sign is a bruit. A bruit is an abnormal sound heard within the arteries of some individuals with carotid artery stenosis. Throughout a physical exam, a healthcare provider may use a stethoscope to listen to the neck near the carotid arteries. A “whooshing” sound, known as a bruit, can indicate decreased blood flow because of atherosclerosis.
Another possible symptom is a transient ischemic attack. A TIA is the same as a stroke but less serious. It still needs prompt medical attention. Symptoms of both a stroke and a TIA include sudden and severe headaches, loss of balance, dizziness, slurred speech or difficulty speaking, vision problems, numbness or weakness in the limbs or face (often in one area of the body), and lack of ability to move single or multiply limbs. Anyone facing these symptoms should seek urgent medical care. Typically, symptoms of a TIA resolve within a day.
A stroke can cause similar symptoms as a TIA but often results in more serious outcomes. A stroke can cause permanent brain damage because of loss of oxygen. This may cause long-term vision problems, speech difficulties, or disabilities. In some cases, a stroke can result in paralysis or death. Immediate emergency medical help is crucial if signs of a stroke or TIA are observed.
Causes and Risk Factors
Carotid artery disease is primarily caused by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. While plaque components are present in the blood, they tend to accumulate in small areas of damage within the arteries. This damage can result from a combination of hereditary factors, as well as lifestyle and dietary alternatives over time.
Several major risk factors contribute to this damage and plaque buildup. Smoking, an unhealthy diet, high cholesterol, and hypertension are significant contributors. Conditions such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity also increase the risk. Additionally, a lack of physical exercise, sleep apnea, and high levels of stress can further exacerbate the problem.
Older age is another risk factor, and having genetics of atherosclerosis can also increase the likelihood of developing carotid artery stenosis.
Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis is crucial to prevent serious complications, like stroke. To diagnose the condition, a healthcare provider will start by discussing the person’s medical history and lifestyle habits. If the healthcare provider suspects a risk of carotid artery stenosis, they may conduct a physical exam and order tests to evaluate blood health.
One part of the physical exam involves listening for a bruit, which is an abnormal sound with the arteries. If a bruit is detected, the healthcare provider will likely recommend additional tests to further investigate.
To examine the carotid arteries and check for narrowing, healthcare providers typically use imaging tests. These tests provide detailed images of the inside of the arteries and help identify any blockages.
Ultrasounds are a common imaging test for carotid artery stenosis. They use sound waves to create pictures of the arteries, helping to release any narrowing.
Angiography is another imaging method that involves injecting a special dye into the arteries. The dye makes the arteries visible on X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans. This test allows healthcare providers to clearly see any narrowing or blockages within the arteries.
Treatment
Effective treatment for carotid artery stenosis is important to decrease the risk of severe complications and prevent the disease from worsening. Treatment strategies typically involve a combination of dietary and lifestyle modifications, medications, and sometimes surgical procedures.
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications
Making dietary and lifestyle modifications is a fundamental part of managing carotid artery stenosis. Healthcare providers often recommend adopting a heart-healthy diet, maintaining a moderate weight, maintaining fitness, and ceasing smoking if applicable. Managing other conditions, like diabetes and heart disease, is also important.
For a heart-healthy diet, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute suggests decreasing the intake of sodium, trans fats, saturated fats, added sugars, and alcohol. Rather, the diet should include plenty of vegetables, fruits, low-fat dairy products, whole grains, lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, poultry, seeds, and nuts.
Medications
In addition to lifestyle changes, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to help manage carotid artery stenosis. Common medications involve blood thinners like clopidogrel or aspirin, which help prevent clotting. Depending on the individual’s specific risk factors, healthcare providers might also prescribe medicines to control lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Outlook
Receiving proper treatment and making positive lifestyle modifications are crucial for improving the outlook for someone with carotid artery stenosis. By following their healthcare provider’s treatment plan and adopting healthier habits, individuals can help prevent the condition from worsening.
Although there is no complete cure for carotid artery stenosis, effective treatment can significantly lower the risk of serious complications, like a stroke. With successful management, individuals can decrease the chances of experiencing major health issues and maintain a better quality of life.
Summary
Carotid artery stenosis is caused by plaque buildup in the arteries that supply blood to the brain. Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent serious complications like stroke. Treatment involves lifestyle changes such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and managing risk factors like hypertension and diabetes.
Medications may also be prescribed to prevent clotting and control cholesterol. While there is no cure for the disease, effective management can reduce the risk of severe events. Following a treatment plan and making positive lifestyle changes can help improve the outlook and quality of life.